Refactoring TypeScript
Source code refactoring can improve the quality and maintainability of your project by restructuring your code while not modifying the runtime behavior. Visual Studio Code supports refactoring operations (refactorings) such as Extract Method and Extract Variable to improve your code base from within your editor.
Visual Studio Code has built-in support for TypeScript refactoring through the TypeScript language service and in this topic we'll demonstrate refactoring support with the TypeScript language service.
Rename
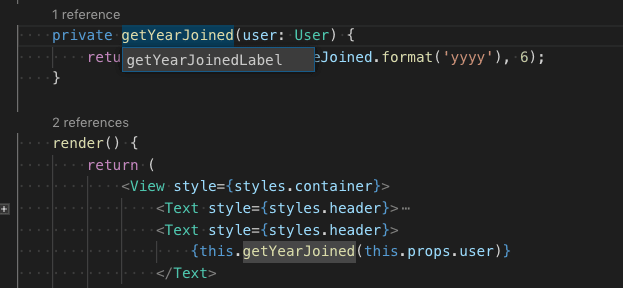
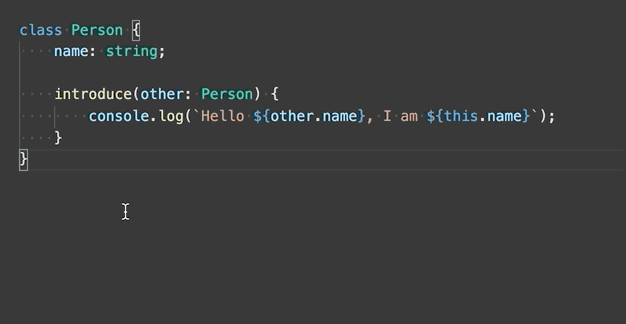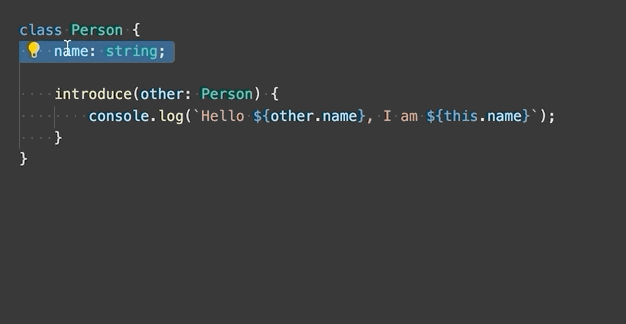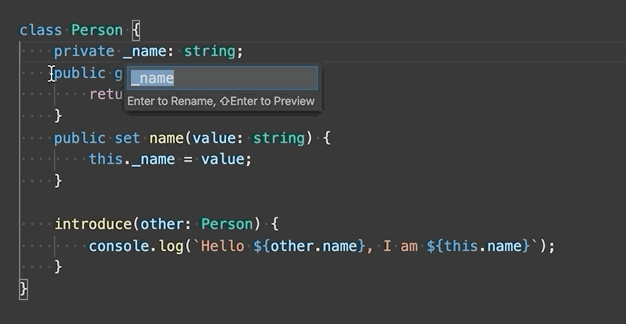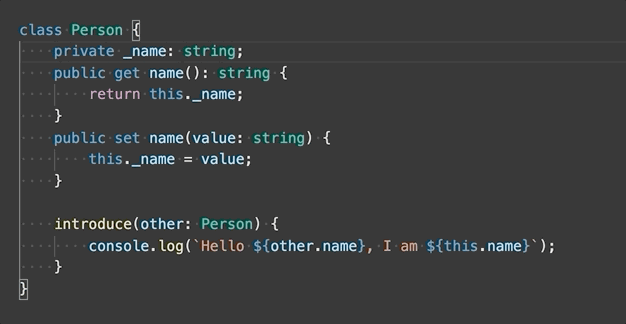
One of the simplest refactorings is to rename a method or variable. Press F2 to rename the symbol under the cursor across your TypeScript project:
Refactoring
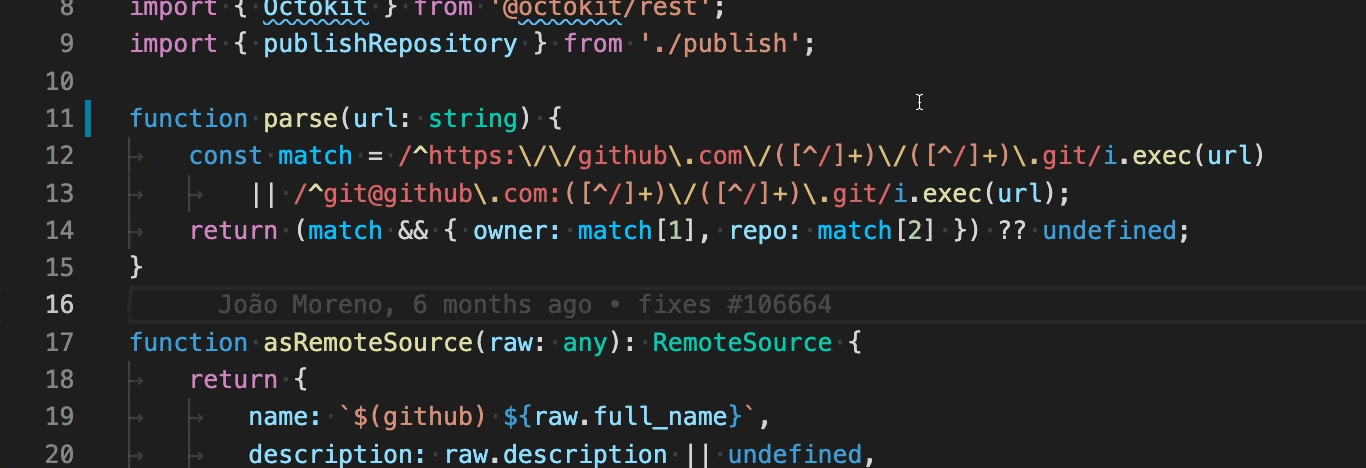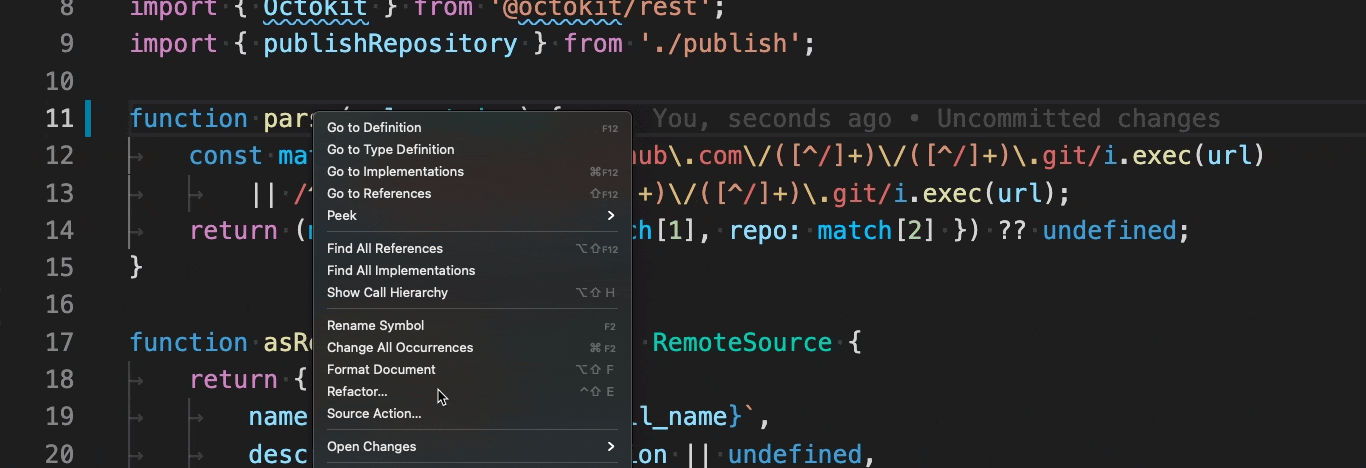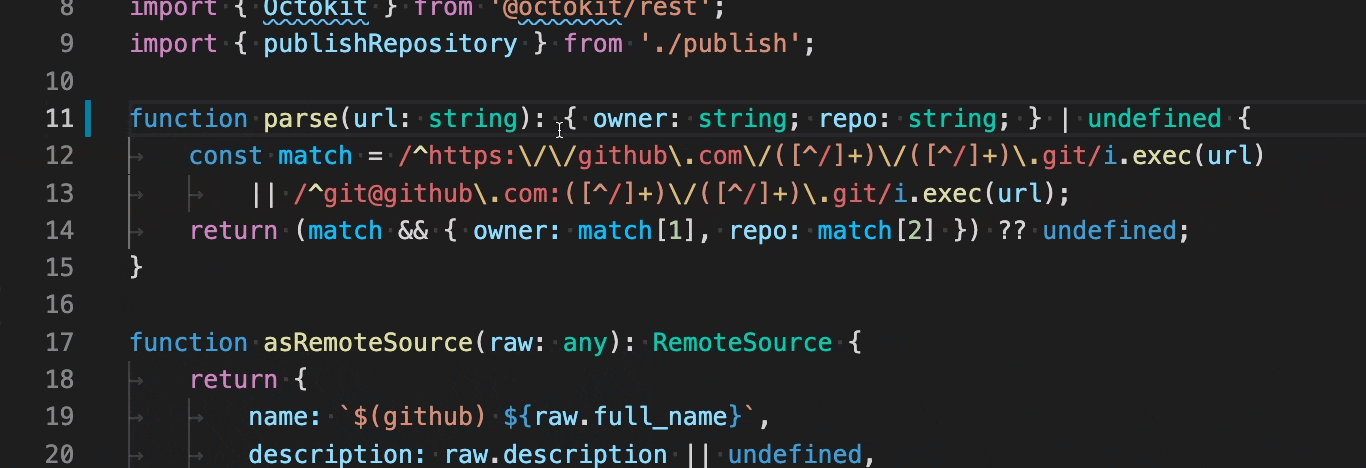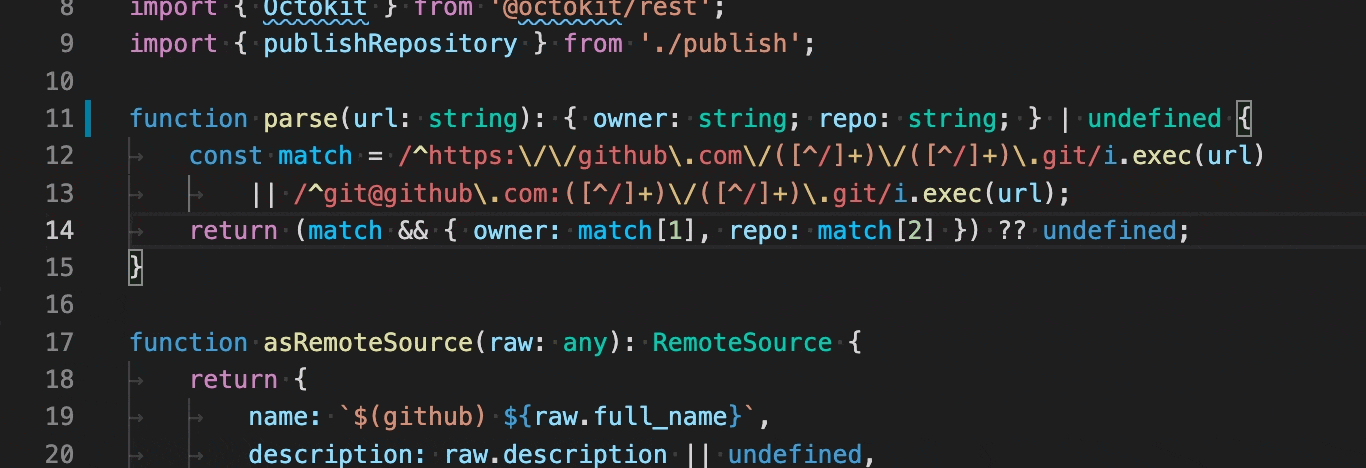
To see the available TypeScript refactorings, put your cursor on a region of your source code and either right-click to bring up the editor context menu and select Refactor or press ⌃⇧R (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+R) directly.
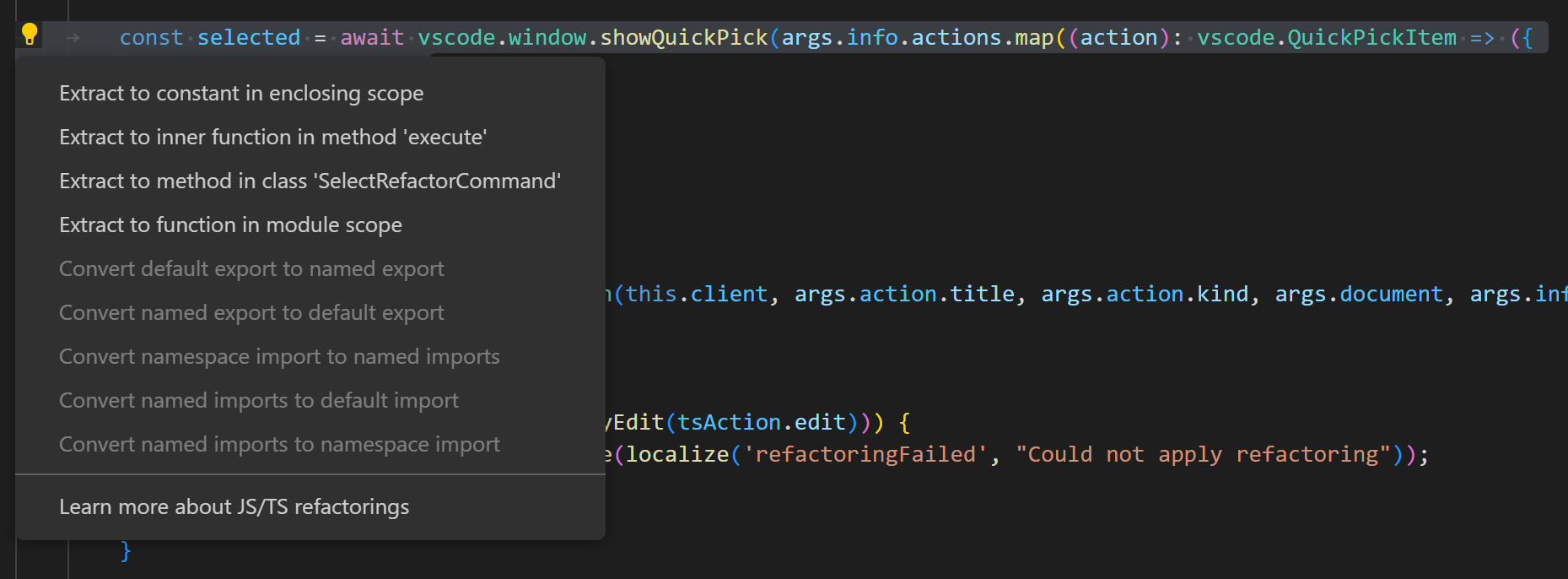
See Refactorings for more information about refactorings and how you can configure keyboard shortcuts for individual refactorings.
Available TypeScript refactorings include:
-
Extract to method or function - Extract the selected statements or expressions to either a new method or a new function in the file.
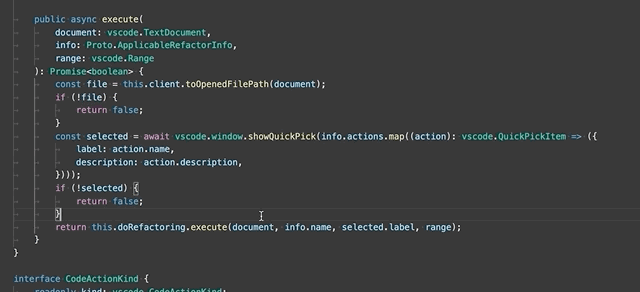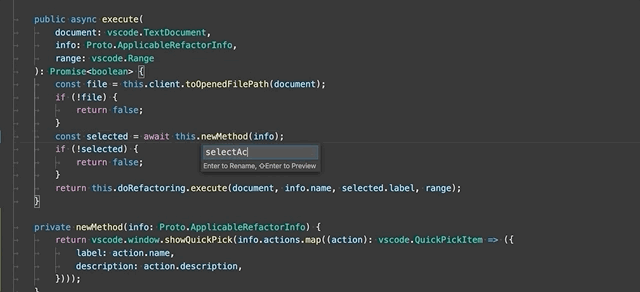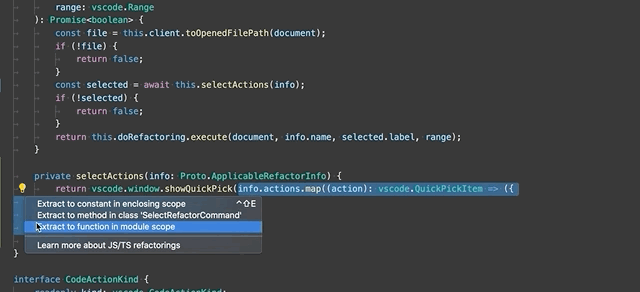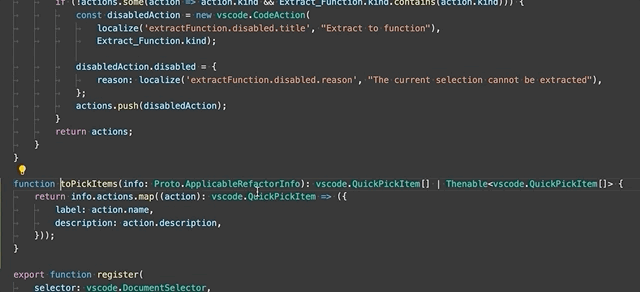
After selecting the Extract to method or Extract to function refactoring, enter the name of the extracted method/function.
-
Extract to constant - Extract the selected expression to a new constant in the file.
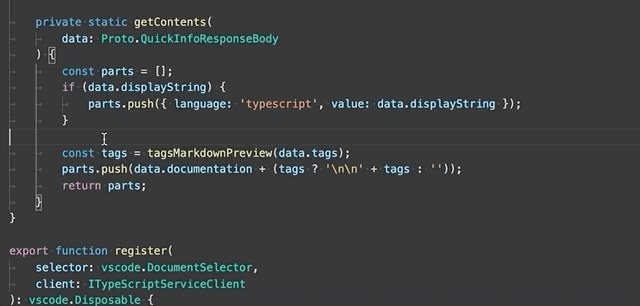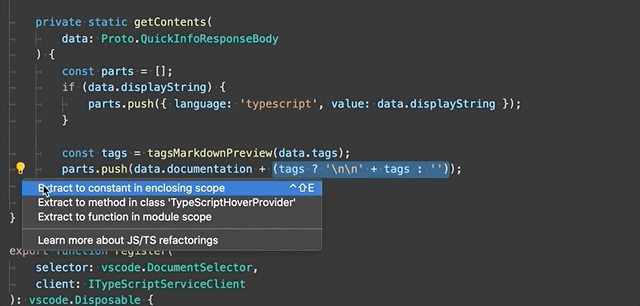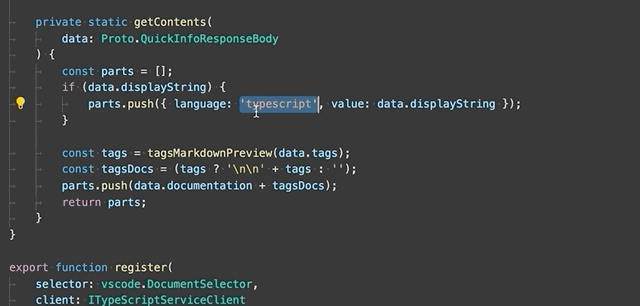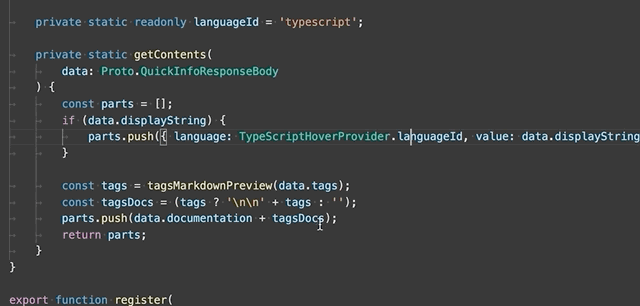
-
Extract type to interface or type alias - Extract the selected complex type to either an interface or a type alias.
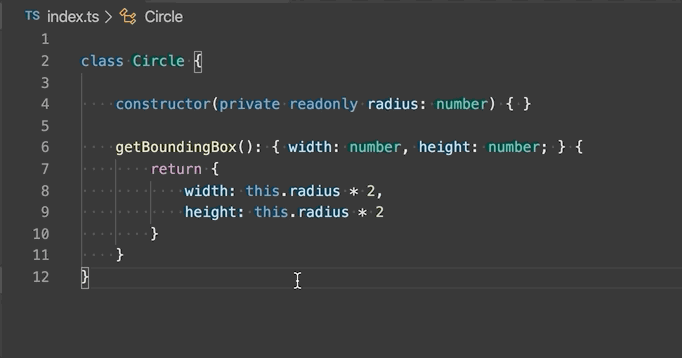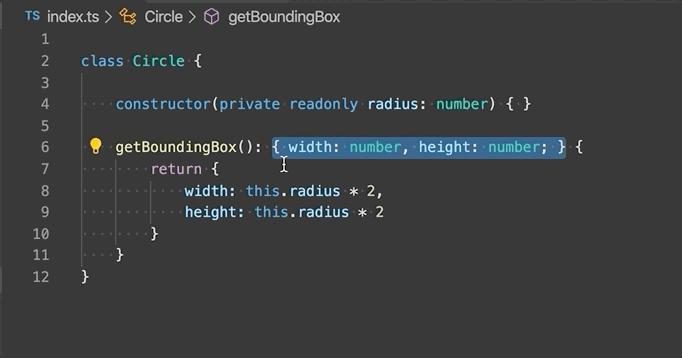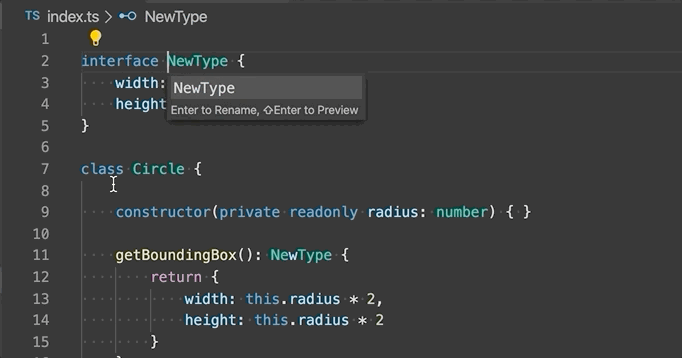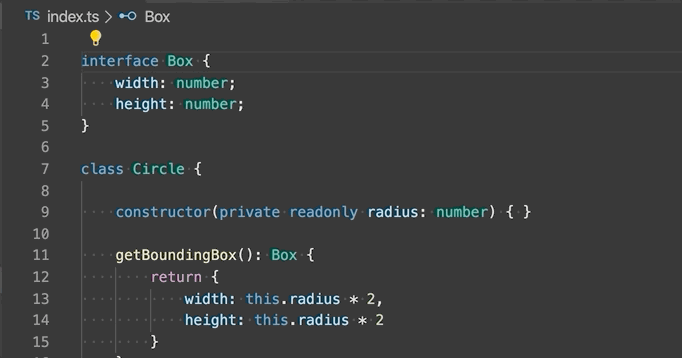
-
Move to new file - Move one or more classes, functions, constants, or interfaces in the top-level scope of the file to a new file. The new file's name is inferred from the selected symbol's name.
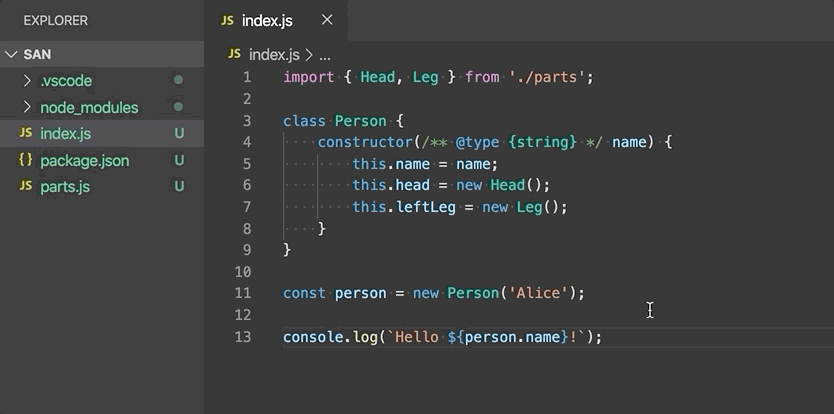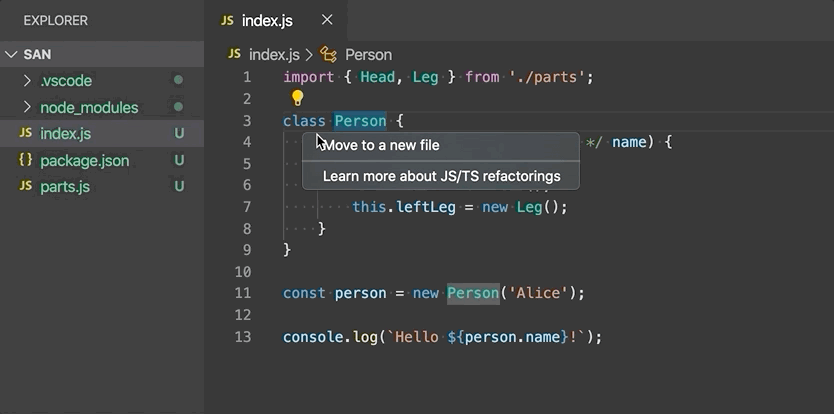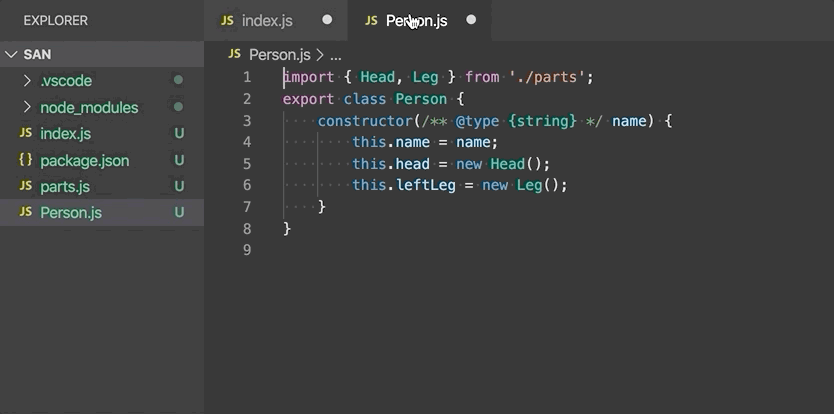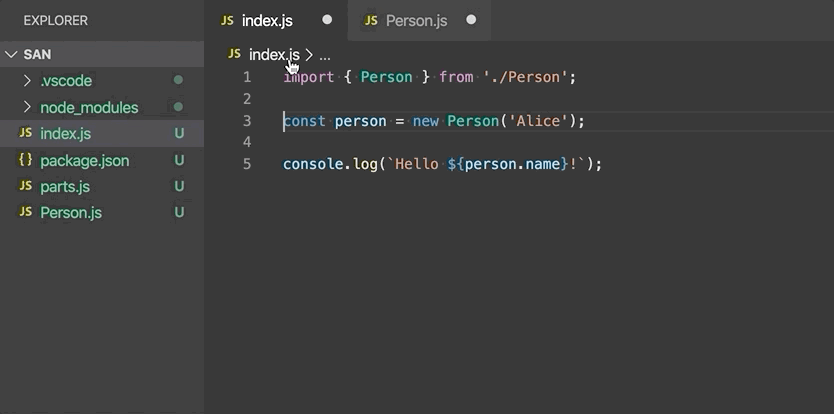
-
Convert between named imports and namespace imports - Convert between named imports (
import { Name } from './foo') and namespace imports (import * as foo from './foo').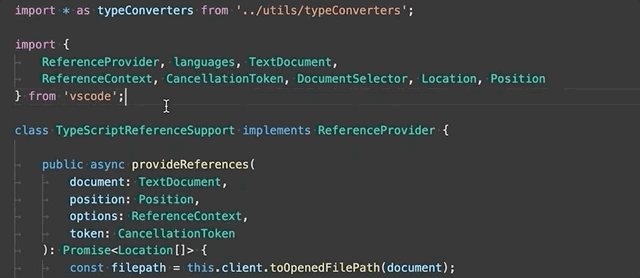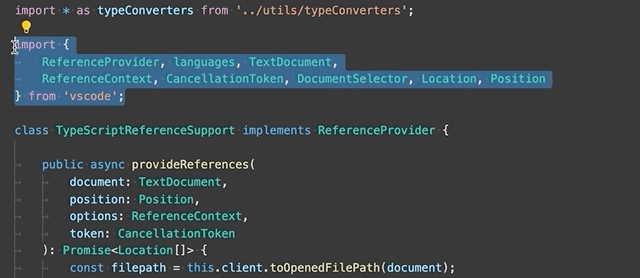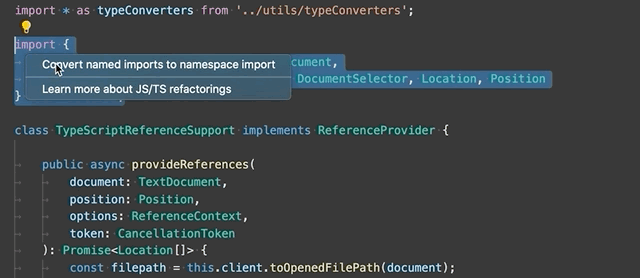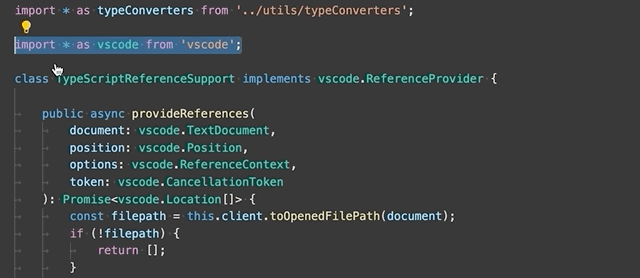
-
Convert between default export and named export - Convert from using a
export defaultand having a named export (export const Foo = ...). -
Convert parameters to destructured object - Rewrite a function that takes a long list of arguments to take a single arguments object.
-
Generate get and set accessors - Encapsulate a selected class property by generating a getter and setter for it.
-
Infer function return types - Adds explicit return type annotations to functions.
-
Add/remove braces from arrow function - Converts single line arrow function to multiline and back.
Quick Fixes
Quick Fixes are suggested edits that address simple coding errors. Example Quick Fixes include:
- Adding a missing
thisto a member access. - Fixing a misspelled property name.
- Removing unreachable code or unused imports
- Declaring
When you move your cursor on to a TypeScript error, VS Code shows a light bulb that indicates that Quick Fixes are available. Click the light bulb or press ⌘. (Windows, Linux Ctrl+.) to show a list of available Quick Fixes and refactorings.
Additionally, Code Action Widget: Include Nearby Quick Fixes (editor.codeActionWidget.includeNearbyQuickFixes) is a setting that is enabled on default, which will activate the nearest Quick Fix in a line from ⌘. (Windows, Linux Ctrl+.) (command ID editor.action.quickFix), no matter where your cursor is in that line.
The command highlights the source code that will be refactored or fixed with Quick Fixes. Normal Code Actions and non-fix refactorings can still be activated at the cursor location.
Unused variables and unreachable code
Unused TypeScript code, such as the else block of an if statement that is always true or an unreferenced import, is faded out in the editor:
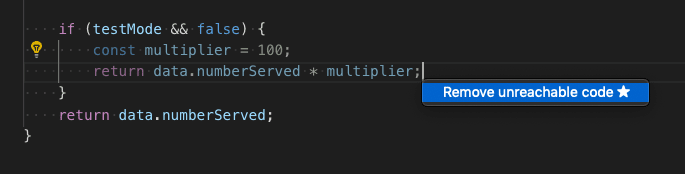
You can quickly remove this unused code by placing the cursor on it and triggering the Quick Fix command (⌘. (Windows, Linux Ctrl+.)) or clicking on the light bulb.
To disable fading out of unused code, set "editor.showUnused" to false. You can also disable fading of unused code only in TypeScript by setting:
"[typescript]": {
"editor.showUnused": false
},
"[typescriptreact]": {
"editor.showUnused": false
},
Organize Imports
The Organize Imports source code action sorts the imports in a TypeScript file and removes unused imports:
You can run Organize Imports from the Source Action context menu or with the ⇧⌥O (Windows, Linux Shift+Alt+O) keyboard shortcut.
Organize imports can also be done automatically when you save a TypeScript file by setting:
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.organizeImports": "explicit"
}
Update imports on file move
When you move or rename a file that is imported by other files in your TypeScript project, VS Code can automatically update all import paths that reference the moved file.
The typescript.updateImportsOnFileMove.enabled setting controls this behavior. Valid settings values are:
"prompt"- The default. Asks if paths should be updated for each file move."always"- Always automatically update paths."never"- Do not update paths automatically and do not prompt.
Code Actions on Save
The editor.codeActionsOnSave setting lets you configure a set of Code Actions that are run when a file is saved. For example, you can enable Organize Imports on save by setting:
// On explicit save, run fixAll source action. On auto save (window or focus change), run organizeImports source action.
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll": "explicit",
"source.organizeImports": "always",
}
As of today, the following enums are supported:
explicit(default): Triggers Code Actions when explicitly saved. Same astrue.always: Triggers Code Actions when explicitly saved and on Auto Saves from window or focus changes.never: Never triggers Code Actions on save. Same asfalse.
You can also set editor.codeActionsOnSave to an array of Code Actions to execute in order.
Here are some source actions:
"organizeImports"- Enables organize imports on save."fixAll"- Auto Fix on Save computes all possible fixes in one round (for all providers including ESLint)."fixAll.eslint"- Auto Fix only for ESLint."addMissingImports"- Adds all missing imports on save.
See TypeScript for more information.
Code suggestions
VS Code automatically suggests some common code simplifications such as converting a chain of .then calls on a promise to use async and await
Set "typescript.suggestionActions.enabled" to false to disable suggestions.
Next steps
Read on to find out about:
- Editing TypeScript - Learn about VS Code editing features for TypeScript.
- Debugging TypeScript - Configure the debugger for your TypeScript project.