Chat overview
Chat in Visual Studio Code enables you to use natural language for AI-powered coding assistance. Ask questions about your code, get help understanding complex logic, generate new features, fix bugs, and more, all through a conversational interface. This article provides an overview of the chat surfaces, how to configure a chat session, add context, write effective prompts, and review AI-generated changes.
Prerequisites
- Access to GitHub Copilot. If you don't have a subscription, you can use Copilot for free by signing up for the Copilot Free plan.
Access chat in VS Code
VS Code provides multiple ways to start an AI chat conversation, each optimized for different workflows. Use the Chat menu in the VS Code title bar or the corresponding keyboard shortcuts.
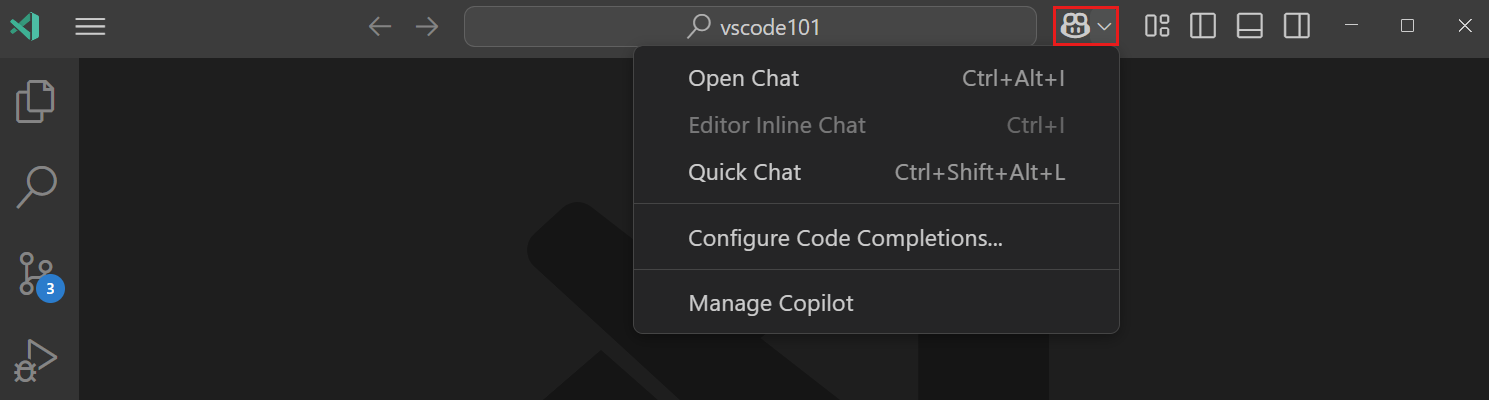
| Surface | Shortcut | Best for | Learn more |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chat view | ⌃⌘I (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Alt+I) | Multi-turn conversations, agentic workflows, multi-file edits. Also available as an editor tab or separate window. | Chat sessions |
| Inline chat | ⌘I (Windows, Linux Ctrl+I) | In-place code edits and terminal command suggestions. | Inline chat |
| Quick chat | ⇧⌥⌘L (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+Alt+L) | Quick questions without leaving your current view. Opens a lightweight chat panel at the top of the editor. | Quick Chat |
| Command line | code chat |
Starting chat from outside VS Code. | CLI docs |
Submit your first prompt
To see how chat works, try creating a basic app:
-
Open the Chat view by pressing ⌃⌘I (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Alt+I) or selecting Chat from the VS Code title bar.
-
Select an agent from the agent picker. For example, select Agent to let chat autonomously determine what needs to be done and make changes to your workspace. Learn more about built-in agents.
-
Type the following prompt in the chat input field and press Enter to submit it:
Create a basic calculator app with HTML, CSS, and JavaScriptThe agent applies changes directly to your workspace and might also run terminal commands, for example, to install dependencies or run build scripts.
-
In the editor, review the suggested changes and choose to keep or discard them.
For a full hands-on walkthrough, follow the agents tutorial.
Send messages while a request is running
Message steering and queuing are experimental features.
You don't have to wait for a response to finish before sending your next message. While a request is in progress, use the dropdown on the Send button to choose how to handle the new message:
- Add to Queue: the message waits and sends automatically after the current response completes.
- Steer with Message: the current request yields and your new message processes immediately.
- Stop and Send: cancels the current request and sends your new message right away.
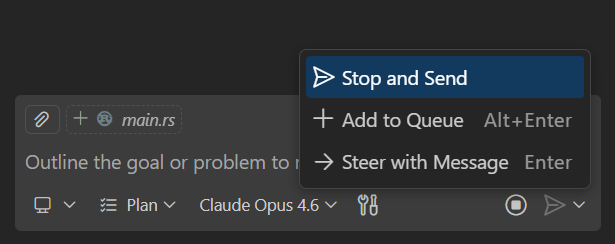
When you have multiple pending messages, drag and drop them to reorder. Learn more about sending messages while a request is running.
Configure your chat session
When you start or adjust a chat session, three choices shape how the AI responds: which agent to use, where the session runs, and which language model powers it.
Choose where to run
Agent sessions can run in different environments to match your workflow. Select the session type from the session type dropdown in the Chat view.
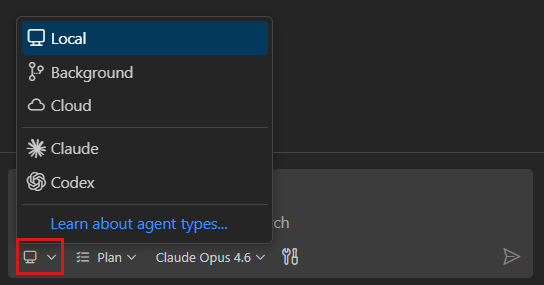
| Session type | Description |
|---|---|
| Local | Runs interactively in VS Code on your machine. Best for exploratory tasks that need immediate feedback. |
| Background | Runs autonomously on your machine via the CLI. Best for well-defined tasks you want to run in the background. |
| Cloud | Runs on remote infrastructure and opens a pull request. Best for team collaboration and well-defined tasks. |
| Third-party | Uses agents from external providers like Anthropic or OpenAI. |
You can hand off a session from one type to another mid-conversation, and the full conversation history carries over. Learn more about agent types and handing off sessions.
Choose an agent
Agents let chat assume a different role or persona optimized for specific tasks. Select an agent from the agents dropdown in the Chat view. You can switch between agents at any time during a session.
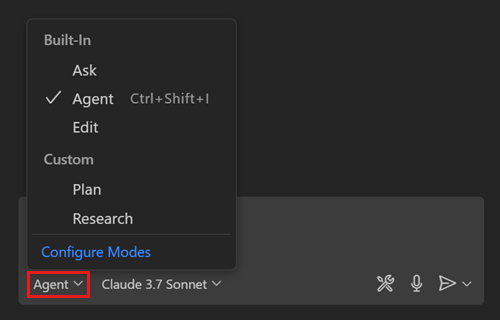
VS Code provides three built-in agents:
- Agent: autonomously plans and implements changes across files, runs terminal commands, and invokes tools.
- Plan: creates a structured, step-by-step implementation plan before writing any code. Hands the plan off to an implementation agent when it looks right.
- Ask: answers questions about coding concepts, your codebase, or VS Code itself without making file changes.
For more specialized workflows, create your own custom agents that define a specific role, available tools, and a language model.
Learn more about the built-in agents and their capabilities.
Choose a language model
VS Code offers different language models, each optimized for different tasks. Some models are designed for fast coding tasks, while others excel at complex reasoning and planning. Use the model dropdown in the chat input field to select the model that best fits your needs.
You can also add models from other providers and use them in chat. Learn more about language models in VS Code.
The list of available models might vary based on your Copilot subscription and might change over time. For more information about the available language models, see the GitHub Copilot documentation.
Add context to your prompts
Providing the right context helps the AI generate more relevant and accurate responses.
-
Implicit context: VS Code automatically includes the active file, your current selection, and the file name as context. When you use agents, the agent decides autonomously if additional context is needed.
-
#-mentions: type#in the chat input to explicitly reference files (#file), folders, symbols, your codebase (#codebase), terminal output (#terminalSelection), or tools like#fetchand#githubRepo. -
@-mentions: type@to invoke specialized chat participants like@vscode,@terminal, or@workspace, each optimized for their respective domain. -
Vision: attach images, such as screenshots or UI mockups, as context for your prompt.
-
Browser elements (Experimental): select elements from the integrated browser to add HTML, CSS, and screenshot context to your prompt.
Learn more about managing context for AI.
Review and manage changes
After the AI makes changes to your files, review and accept or discard them.
-
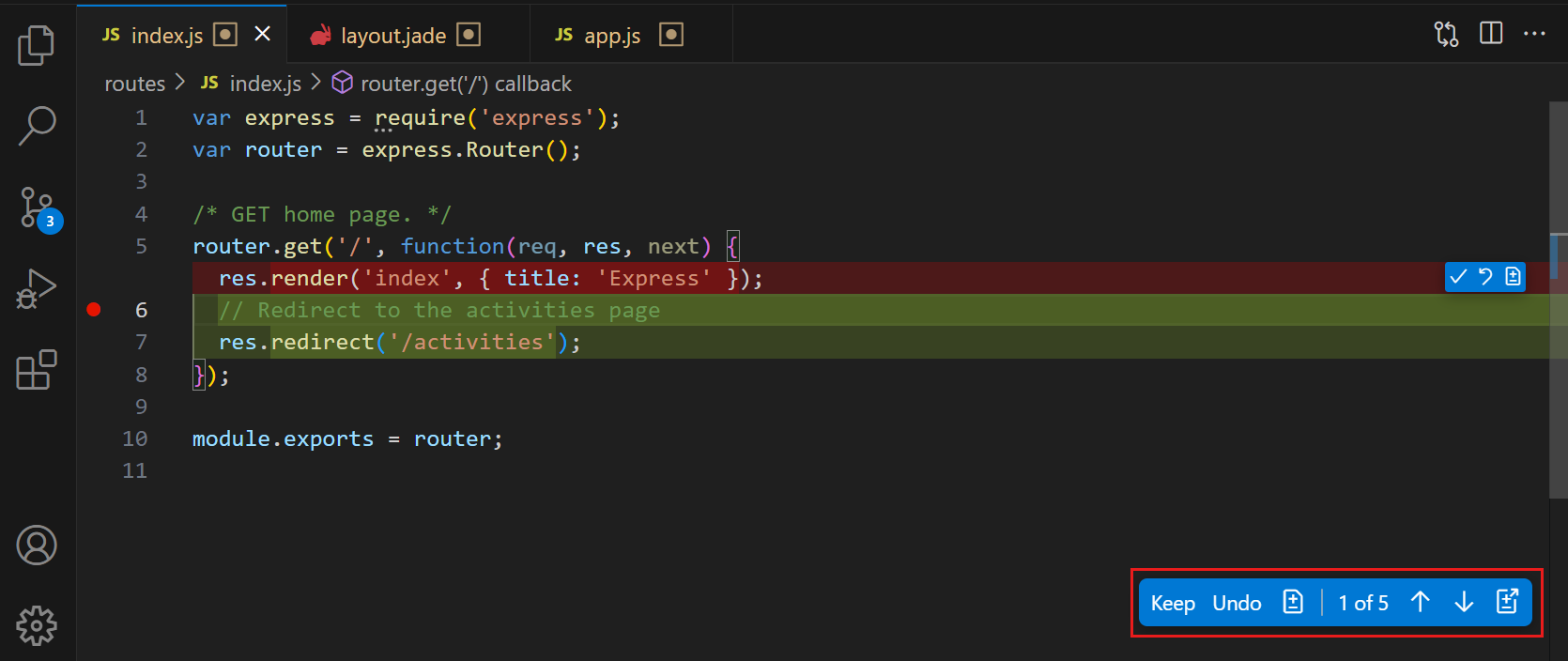
Review inline diffs: open a changed file to see inline diffs of the applied changes. Use the editor overlay controls to navigate between edits and Keep or Undo individual changes. For more information, see reviewing AI-generated code edits.
-
Use checkpoints: VS Code can automatically create snapshots of your files at key points during chat interactions, enabling you to roll back to a previous state. For more information, see checkpoints and editing requests.
-
Stage to accept: staging your changes in the Source Control view automatically accepts any pending edits. Discarding changes also discards pending edits.
Get better responses
Chat provides several ways to improve the quality and relevance of AI responses:
-
Write effective prompts: be specific about what you want, reference relevant files and symbols, and use
/commands for common tasks. Get inspired by prompt examples or review the full prompt engineering guide. -
Customize the AI: tailor the AI's behavior to your project by adding custom instructions, creating reusable prompt files, or building custom agents for specialized workflows. For example, create a "Code Reviewer" agent that provides feedback on code quality and adherence to your team's coding standards.
-
Extend with tools: connect MCP servers or install extensions that contribute tools to give the agent access to external services, databases, or APIs.
For more information, see customizing AI in VS Code.
Troubleshoot chat interactions
Use the Chat Debug view to inspect the details of AI requests and responses. The view shows the system prompt, user prompt, context sent to the language model, and tool invocations for each interaction. This is useful for understanding why the AI responded in a certain way or for troubleshooting unexpected results.